How Value Stream Mapping Helps Eliminate Waste
It’s good to have transparency in every business. When you have a clear understanding of how your business process works, it helps make the process better. When you are providing a product or a service for your customer, the customer only thinks about the value of the product or the service. A business operation with less wasted value turns out to be an efficient and moneymaking one.
This whole procedure of understanding the value of your process is called value stream mapping (VSM). In this post, I will be telling you what exactly value stream mapping is and why it is important.
What Is Value Stream Mapping?
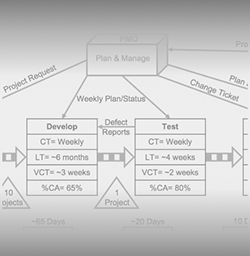
Value stream mapping is the process of creating an easy-to-understand format of the workflow using visualizations. Imagine that you have a business that builds a product for your customers. Product development has different steps in it. Each of these steps adds some value to the final product. When you use value stream mapping, it is easy for you to understand which step of the process adds how much value to the complete system.
Why Do You Need Value Stream Mapping?
Value stream mapping is a great way to optimize your process cycle and make it more efficient. Value stream mapping helps you understand where there is waste in the product development system. This, in return, helps you plan on how to get the waste reduced or eliminated. You’ve seen this word “waste” a couple of times in this post. Now, let me tell you what this waste is.
What Is Waste?
Waste is basically any step in the process that doesn’t add value to the whole system. You’d understand waste better if I explain the types of waste, so I’ll get right into it. The different types of wastes are as follows:
Waiting
This is the waste that occurs when the process has stopped because it is waiting for the next step to start. One simple example would be when an industry is waiting for raw materials.
Transportation
This is the waste that occurs during the transportation of materials or people. Though the materials and people add value to the process, transportation by itself adds no value.
Motion
Motion waste is generated when a person has to make unnecessary movements. Suppose a step in a process requires using two machines. If these two machines are placed at a distance, then the person walking between the machines can be considered motion waste.
Inventory
If there is more supply than demand, the inventory gets full. Having more inventory than the ideally required amount is a waste because it adds to inventory costs.
Defects
Defects are the waste that occurs when the product is not good enough to be provided to the customer. These can occur due to machine failure, human errors, transportation issues, etc.
Unused Talent
This waste occurs when the employee is being underused. Suppose a person can work on 10 products per day, but they are being allocated to work on only 8 products. It would result in unused talent.
Overprocessing
Over processing occurs when the process develops a product of higher quality than is required. Suppose you have to develop a product of quality X. Developing a product of quality X+Y is a waste.
Overproduction
This is the waste where the business develops more products than actually required. The extra products will be of no use and hence it is a waste.
Now that you know what the different types of waste are, let me tell you how value stream mapping helps in waste management.
How Does Value Stream Mapping Help in Waste Management?
When you have a clear understanding of the different kinds of waste occurring in your process and the points where they are occurring, it is easy to manage waste. You can come up with strategies to reduce waste. You can also slightly change the process if that helps manage waste without requiring a lot of effort.